Data Analysis and Programming 📊💻
Fundamentals of AI-Driven Algorithm Development and Data Science
Programming is about getting a computer to do what you (the user) want it to do. It’s about trying to make the future less painful. It’s about making things easier for our teammates. It’s about getting things wrong and being able to bounce back. It’s about forming good habits. It’s about understanding your toolset. The Pragmatic Programmer, 2020
Syllabus
Welcome to Data Analysis and Programming (DAP)!
In this book, you will find all the information you need to succeed in the course.
General Information
- Level: Bachelor of Science
- Faculty: Behavioural, Management and Social Sciences (BMS)
- Module: 202300167 (see on Osiris)
- Credits (ECTS): 3
- Lecturer: Breno Alves Beirigo (b.alvesbeirigo@utwente.nl) / About
📜Course Description
This course introduces students to
- essential data analysis techniques and
- computer programming fundamentals.
Essential data analysis techniques
Students will learn basic- and intermediate-level features of spreadsheet software such as MS Excel and Google Sheets, covering topics like
- tables,
- pivot tables,
- graphs,
- formula manipulation,
- worksheet layout,
- (conditional) formatting,
- proposition logic in formulas, and
- use of basic formulas for data retrieval and manipulation.
They will also develop the programming skills necessary to perform data analysis using Python libraries such as Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib, enabling them to automate processes and extract insights from large datasets.
Computer programming fundamentals
Students will be introduced to Python programming, focusing on real-world Industrial Engineering & Management problems. The course covers essential concepts such as
- functions,
- arguments,
- return values,
- variables,
- data types,
- conditionals,
- Boolean expressions,
- loops,
- exception handling,
- bug fixing,
- unit testing, and
- utilizing third-party libraries.
🎯Course Aims
This course prepares students for more advanced programming languages and concepts typically encountered in the MSc stage of engineering programs. The aims are as follows:
- To introduce students to data analysis using Python libraries and spreadsheet software.
- To equip students with the ability to write, test, and debug Python code effectively.
- To develop students’ understanding of fundamental programming concepts, including functions, variables, conditionals, and loops.
- To foster students’ skills in utilizing third-party libraries, handling exceptions, and fixing bugs.
- To enhance students’ file handling operations and reading/writing data proficiency.
🧠Learning Objectives
By the end of this course, students will be able to:
- Perform data analysis tasks (cleaning, manipulation, visualization) using spreadsheet software and Python libraries to extract insights and make informed decisions.
- Demonstrate a solid understanding of Python syntax, including variables, data types, and operators.
- Write and execute Python code to implement various functions, using appropriate arguments and return values.
- Utilize conditionals and Boolean expressions to control the flow of program execution.
- Employ loops effectively to perform repetitive tasks and iterate over data structures.
- Handle exceptions and debug Python code to identify and resolve errors.
- Write unit tests to verify the correctness of their code and ensure robustness.
- Access and utilize third-party libraries to leverage pre-existing functionality.
- Read and write data to files using Python’s file-handling capabilities.
⏳Study Load (ECTS)
The DAP course has a total study load of 3 ECTS1 (84 hours). Table 1 shows the estimated study load per activity.
The activities are as follows:
- Lecture: New concepts are introduced; lectures can be in-person or online.
- Tutorial: Aimed at practicing concepts introduced in lectures and solving assignments.
- Q&A Session: A session for asking questions about the course content right before the exam.
- Exam Review: A session to review exam results and discuss solutions. You will have the chance to inspect your exam and compare your answers with the correct ones.
- Self-study: Additional study time may be required to understand and complete the assignments.
- Exam Preparation: Time allocated for studying the course content and preparing for exams.
- Exam: An exam is held in a computer lab. You will submit your answers using a Chromebook provided by the university.
| Activity | Count | Duration (h) | Workload (h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lectures | 1 | 1.75 | 1.75 |
| Tutorials | 10 | 1.75 | 17.50 |
| Exam Reviews | 1 | 1.75 | 1.75 |
| Self-study | 10 | 5.00 | 50.00 |
| Exams | 1 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| Total | 84 |
Note that the workload breakdown of the activities post-exam is not included in Table 1. These are as follows:
- Exam Inspection and Review: 1 session × 1.75 hours = 1.75 hours
- Resit Exam: 1 exam × 3 hours = 3.00 hours
- Resit Exam Inspection and Review: 1 session × 1.75 hours = 1.75 hours
📅 Content Overview (Tentative)
The content overview for the course is included below. Why tentative? The course is designed to be flexible and adaptive to the group’s needs. Therefore, based on the students’ progress and feedback, adjustments may be made to the schedule and content. The official week-by-week content will be released on Canvas under the “Modules” section.
Why is the content structured in this way?
- The content is divided into three parts.
- Part 1. We will cover basics of algorithm development, Python programming, and conditionals, along with all the essential tools you need for assignments and projects. The aim is to provide you with a solid foundation so you are not hindered by technicalities.
- Part 2. We will cover loops and data structures, topics students often struggle with.
- Part 3. We will cover Data Analysis with Pandas and Excel, reading and writing files, and organizing files. The aim is to provide you with the tools you need to work with data and files in a professional setting.
Are assignments, exercises, and projects mandatory?
- No, but they are highly recommended. The deadlines are set to help you manage your time and indicate when it is best to have completed the content so you are prepared for the next week.
Shall I use AI when working on the assignments?
- Only when you can’t find a solution on your own. Please turn off the AI when you are working on the assignments and turn it on only when you are stuck. The aim is to learn by doing, not by copying.
Why auto-graded assignments?
- The auto-graded assignments are a primer on TDD (Test-Driven Development). In professional software development, TDD is a common practice. The goal is to write tests before writing the code. This way, you know what you aim for and can test your code as you write it. The auto-graded assignments are a way to introduce you to this practice and provide immediate feedback on your code. Imagine you are working on a project and want to test a new feature. If you have a test suite (i.e., a set of tests that you can run to check if the feature does what it is supposed to do and doesn’t break anything else), you can run the tests and see if the feature works as expected. If the tests pass, you can be confident that when your code is deployed (i.e., made available to users), it will work as expected. If the tests fail, you know that something is wrong, and you can fix it. If you inspect the auto-graded assignments, you will see how the tests are written (check for the
test_functions and theassertstatements).
- The auto-graded assignments are a primer on TDD (Test-Driven Development). In professional software development, TDD is a common practice. The goal is to write tests before writing the code. This way, you know what you aim for and can test your code as you write it. The auto-graded assignments are a way to introduce you to this practice and provide immediate feedback on your code. Imagine you are working on a project and want to test a new feature. If you have a test suite (i.e., a set of tests that you can run to check if the feature does what it is supposed to do and doesn’t break anything else), you can run the tests and see if the feature works as expected. If the tests pass, you can be confident that when your code is deployed (i.e., made available to users), it will work as expected. If the tests fail, you know that something is wrong, and you can fix it. If you inspect the auto-graded assignments, you will see how the tests are written (check for the
W46 (1/10) - Setting Up and Introduction
- Syllabus
- Algorithm Development
- Environment setup: Python, VS Code, GitHub
- Python Basics:
- Exercises on Python Basics and Version Control: (See Canvas)
W47 (2/10) - Python Basics
- Python Basics:
- Modules and Packages
- Exercises on Manipulating Strings: (See Canvas)
- Level Up!
W48 (3/10) - Conditionals
- Flow Control - Conditionals
- Debugging (Except for
try-except) - Exercises on Conditionals: (See Canvas)
- Practice problems and MCQs
- Level Up!
W49 (4/10) - Flow Control - Loops
- Flow Control - Loops
- Exercises on Loops: (See Canvas)
- Practice problems and MCQs
W50 (5/10) - Data Structures
- Data Structures:
- Exercises on Lists: (See Canvas)
- Practice problems and MCQs
- Level Up!
W51 (6/10) - Advanced Data Structures
- Data Structures:
- Exercises on Dictionaries: (See Canvas)
W52 - Holiday
- No activities
W1 - Holiday
- No activities
W2 (7/10) - Data Analysis with Pandas
- Data Analysis with Python Pandas:
- Quickstart: 10 minutes to pandas and Colab
- Assignment: NYC Taxi Data Analysis (See Canvas)
- Level Up!
W3 (8/10) - Data Analysis with Excel
- Data Analysis with Excel
- Assignment: NYC Taxi Data Analysis - Excel (See Canvas)
W4 (9/10) - File Manipulation
- File Manipulation
- Exercises on File Manipulation: (See Canvas)
W5 (10/10) - Q&A & Exam
Tutorial
📝 Exam - Chromebook, in person
Content covered in the exam:
- Algorithm Development
- Python Basics: Intro, Variables, Operators
- Functions
- Modules and Packages
- Conditionals
- Loops
- Data Structures:
- Data Analysis:
- File Manipulation
W6 - Exam Review
W7 - No activities
W8 - No activities
W9 - Resit
- Same topics as the regular exam.
Check TimeEdit for the exact logistics of the resit and any updates after week 5.
✍️ Exams and Grading
This course will be assessed through one 3-hour exam, totaling 100 points. The exam will be conducted in-person using Chromebooks provided by the university and will encompass the entire course content. You will need to score a minimum of 50 points to pass the course.
Grade Calculation Formula
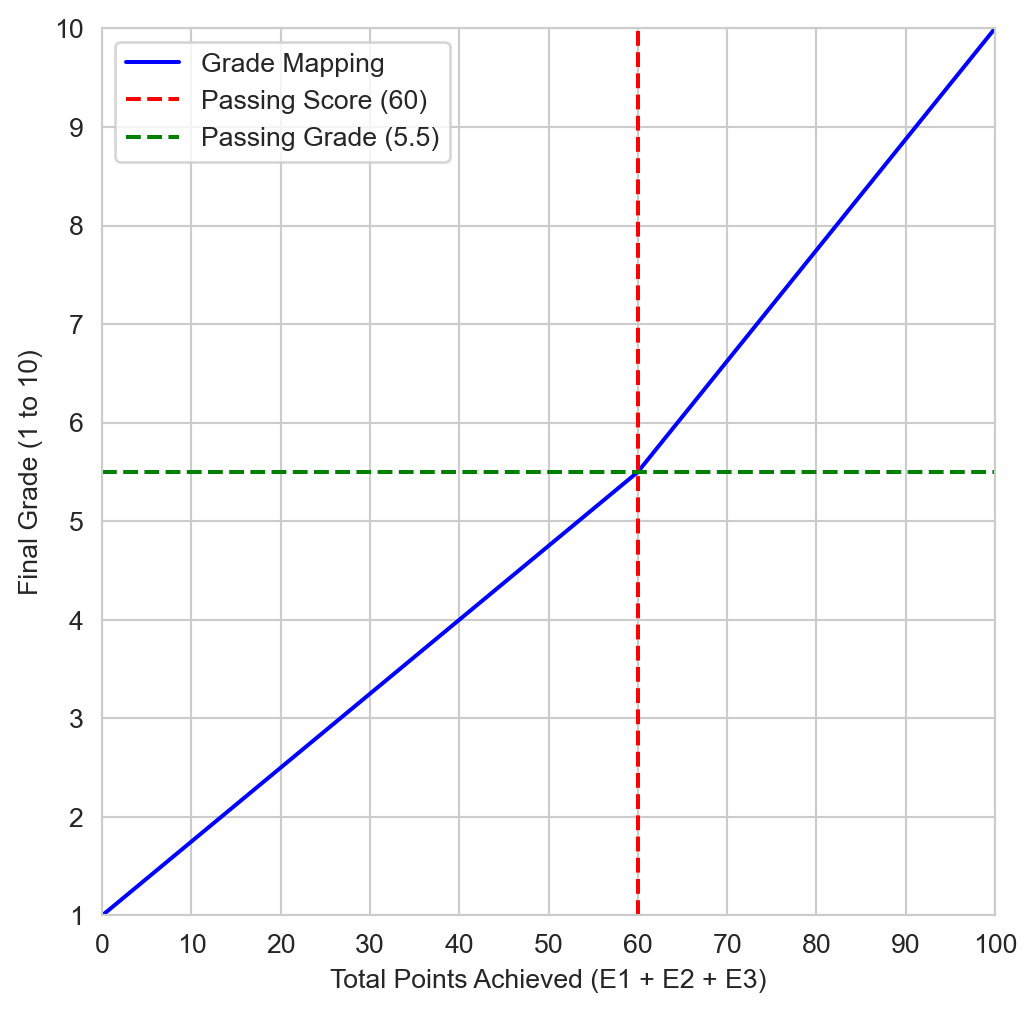
At UT, the grading system is based on a scale from 1 to 10, with 5.5 being the passing threshold. Let \(c = 50\) be the cutting score and \(t = 100\) the total points available. The grade calculation formula is as follows.
If \(p \leq c\) (i.e., the student scored below or equal to the cutting score), the grade is calculated as:
\[ \begin{aligned} G \quad = \quad & 1 + \left( \frac{p}{c} \right) \times 4.5. & \\ \end{aligned} \]
If \(p > c\) (i.e., the student scored above the cutting score), the grade is calculated as:
\[ \begin{aligned} G \quad = \quad & 5.5 + \left( \frac{p - c}{t - c} \right) \times 4.5. & \\ \end{aligned} \]
Therefore:
\[ G = \begin{cases} 1 + \left( \dfrac{p}{50} \right) \times 4.5 & \text{if } p \leq 50 \\ 5.5 + \left( \dfrac{p - 50}{50} \right) \times 4.5 & \text{if } p > 50 \end{cases} \tag{1}\]
In Figure 1, you can see the mapping of total points achieved to the final grade.

Resit Exam
If a student fails to pass the course, they will have the opportunity to take a resit exam. The resit exam will cover the entire course content and will be graded out of 100 points. The content and format of the resit exam will be similar to the final exam. The final grade will be calculated based on the resit exam score using Equation 1.
📋Assessment Format and Style
The exam format will be a digital Chromebook closed-book exam. It consists of two main components:
- Data Analysis with Excel Questions: You will be asked to perform data analysis tasks using Microsoft Excel. This may include data manipulation, creating charts, and performing calculations.
- Practical Programming Questions: You will be asked to write Python code to solve specific problems. This may include writing functions, working with data structures, and implementing algorithms.
Exam Workflow
When the Chromebook starts up, the following tabs will be open:
- Remindo: Open the exam in Remindo and start it.
- Virtual Machine: A virtual machine with the software required to complete the exam is provided. Use it to start a new project and write your code. Save the files in your designated directory.
- Exam Instructions and Questions: Use the table of contents to navigate between questions.
- Python Compiler: As a backup to VS Code, you can use an online Python compiler to test your code. The compiler is available at Programiz.
Follow these steps to complete the exam:
- Read the exam instructions and questions.
- Start the exam in Remindo.
- Solve the data analysis with Excel questions:
- In the tab with the virtual machine:
- Download the Excel file from Remindo to drive
DigitalExams><Student ID>. Files in this directory are backed up automatically. However, you must save your work regularly. - Complete the tasks as instructed.
- Upload the required file(s) to Remindo.
- Download the Excel file from Remindo to drive
- In the tab with the virtual machine:
- Solve the practical programming questions:
- In the tab with the virtual machine:
- Open the VS Code editor (Windows Start Menu > Visual Studio Code).
- Start a new project and write your code.
- Save files in drive
DigitalExams><Student ID>. Files in this directory are backed up automatically. However, you must save your work regularly. - Copy the content of your code to the Remindo text editor.
- Alternatively, use the online Python compiler:
- Write your code in the online compiler Programiz.
- Copy your progress to the Remindo text editor.
- In the tab with the virtual machine:
- Submit your exam in Remindo upon completion.
To ensure fairness and consistency, the exam will be autograded. This means that your code will be automatically evaluated based on predefined criteria. Therefore, it is essential to follow the instructions carefully and ensure that your code meets the requirements specified in the exam questions.
The automatic grading system will evaluate your code based on the correctness of the output: if your code produces the expected output, you will receive full credit; otherwise, you will receive partial credit based on the number of correct outputs.
For example, suppose you are asked to write an algorithm to find the maximum value in a list of numbers. Let’s assume five test cases are provided, each with a different list of numbers L. The expected output for each test case is as follows:
| Test Case | List L |
Expected Output |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] |
5 |
| 2 | [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] |
5 |
| 3 | [-1, -2, -3, -4, -5] |
-1 |
| 4 | [1] |
1 |
| 5 | [] |
None |
If your code produces the correct output for the first three test cases but fails for the last two, you will receive partial credit based on the number of correct outputs. In this case, you will receive 60% (i.e., 3/5) of the total points available for this question.
📚Materials
💻Python programming
📊Data analysis
🤖 Policy on Generative AI
In this course, we encourage the use of Generative AI, such as ChatGPT, to assist with your coding. However, we expect you to use it as a tool to help you understand the concepts, not as a replacement for your learning process. AI gives you the power to quickly test new ideas, but it is your responsibility to understand the concepts behind them and apply them correctly in the right context.
You may treat AI as a “virtual TA” that can help you with coding and debugging3.
For debugging, you can use AI to help you understand error messages and suggest possible solutions. However, you should always strive to understand the error and the solution yourself.
The focus on understanding is crucial, as the exams will test your comprehension of the concepts and your ability to generate code.
Prompt Examples for an AI Tutor
The following are examples of prompts you can use with an AI tutor:
- “What does this error message mean?”
- “How can I fix this error?”
- “What does this code do?”
- “How can I improve this code?”
- “What is the best way to implement this feature?”
- “What is the output of this code?”
- “How can I optimize this code?”
- “What is the best way to structure this code?”
- “What is the best way to debug this code?”
- “What is the best way to test this code?”
- “What is the best way to document this code?”
- “What is the best way to refactor this code?”
These prompts can help you use AI as a tool to enhance your learning experience. It has been shown that if you ask AI to explain the code “step-by-step,” it can help you understand the code better.
Getting Started with AI
If you are new to using AI for coding, here are some tips to get started:
- Start Small: Begin with simple prompts and gradually increase the complexity.
- Ask Questions: Use AI to answer specific questions you have about the code.
- Understand the Output: Make sure you understand the AI-generated code and the reasoning behind it.
AI Tools
There are several AI tools available that can assist you with coding:
- GitHub Copilot: An AI pair programmer that suggests code completions. The Pro version is available for free to students through GitHub Education. We will use GitHub Copilot in this course.
- ChatGPT: A conversational AI that can help explain concepts, debug code, and provide coding examples.
- Claude: Another conversational AI assistant useful for code explanations and problem-solving.
Guidelines for Study Periods
- Permitted Use: Students are allowed to use generative AI tools for learning, understanding concepts, and coding practice.
- Understanding Over Copying: Emphasis should be on understanding the AI-generated solutions, not just copying them. Students should be prepared to explain how and why a particular solution works.
Guidelines for Assessment Periods
- Prohibited Use: The use of generative AI tools is strictly prohibited during assessments, tests, and exams.
- Penalty for Misuse: Any use of AI tools during assessments will be considered academic misconduct and subject to penalties as per the institution’s academic integrity policy.
Priming the Answers
Sometimes, you may want to prime4 the AI to get better answers. Otherwise, the AI may return code that is too advanced or hard to understand.
The following is a series of directives you can use to prime the AI for better answers. You can copy and paste them into the chat window before asking your question.
I am learning to code in Python and want you to follow the guidelines below when generating code snippets for me:
- Use only beginner-level Python syntax. Avoid advanced features like decorators, context managers, or complex object-oriented programming.
- Explain what the code does before the code block. Include a short summary of the script’s purpose.
- Add explanatory comments for every section of the code, including:
- The purpose of the function or script
- What each block of logic does
- Why certain methods or functions are used
- Use simple and descriptive variable names (e.g.,
total_amount,user_name).- Use only basic control structures:
if/elif/else,for,while,input(),print().- Avoid advanced constructs like comprehensions, generators,
try/except,withstatements, or complex data structures beyond basic lists and dictionaries.- Use explicit, expanded syntax. Avoid compact one-liners or chained operations.
- Keep each line of code short and readable. Break long expressions into multiple lines using proper Python indentation.
- Avoid shorthand or Pythonic idioms. Write everything explicitly for clarity.
- Ensure the code is ready to run in a standard Python environment without requiring additional setup.
- Use only built-in Python functions and standard library modules. Avoid external packages unless explicitly requested.
ECTS: European Credit Transfer System. One ECTS is equal to 28 hours of study.↩︎
The book uses the Mu Editor, which is a simple Python editor for beginner programmers. In this course, we use the Visual Studio Code.↩︎
Debugging refers to the process of identifying and fixing errors in code. It is an essential skill for programmers to develop.↩︎
Priming is the process of preparing the AI to provide better answers by giving it specific instructions or context. It helps the AI understand your needs and generate more relevant responses.↩︎