2 Why Python?
Python is a versatile programming language that is widely used in various fields, from web development to scientific computing. Here are some reasons why Python is a popular choice for beginners and professionals alike:
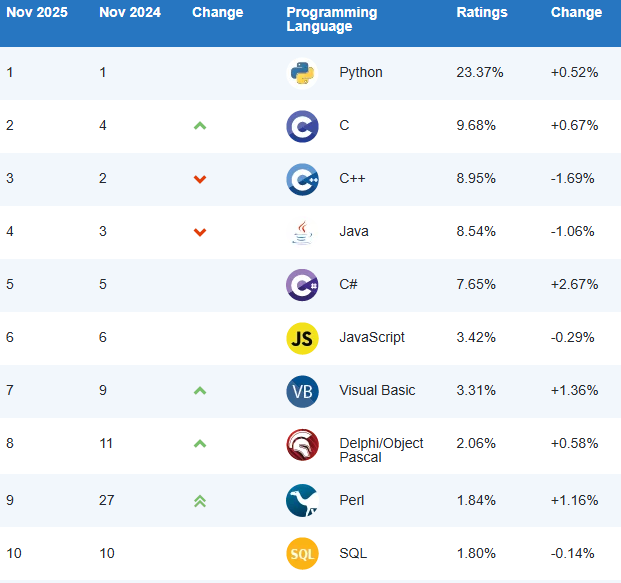
- Ranked among the top programming languages (see Figure 2.1).
- Popular in diverse fields: scientific computing and academic research, web development, data science, AI.
- Beginner-friendly: simple, readable syntax.
- Extensive libraries and frameworks: NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, Django, Flask, TensorFlow, PyTorch.
- Strong community support: forums, tutorials, documentation.
2.1 Disadvantages
Python is not without its drawbacks. Since it is an interpreted language (i.e., executed line by line by an interpreter, without prior compilation), it may not be as fast as compiled languages like C or C++. However, Python can be optimized using libraries like NumPy and Cython, which implement performance-critical code in C. Also, there have been improvements in Python’s performance over the years. Figure 2.2 illustrates the performance difference between Python and other programming languages using a simple example of nested loops.
2.2 Python in the IEM Program
In the IEM program, you will work with several MILP solvers, such as Gurobi and CPLEX, which have Python APIs. You will also use Python libraries like NumPy, Pandas, and Matplotlib for data analysis and visualization.