4 Writing Python Code
To program in Python, you need an IDE or code editor. These are applications that provide tools to help you write and test your code productively (otherwise, you would be writing code in a text editor and running it in the terminal).
- Integrated Development Environment (IDE): An IDE is a software application that provides comprehensive facilities to computer programmers for software development. For example, it includes a source code editor, build automation tools, and a debugger. Most modern IDEs also include support to AI tools, such as code completion, code refactoring, and debugging.
- Code Editor: A code editor is a text editor program designed specifically for editing source code of computer programs. Differently from IDEs, code editors are lightweight and fast, focusing on writing code and not on providing a full development environment.
- Notebooks: Notebooks are interactive documents that allow you to write and execute code, visualize data, and write text. It is based on a programming paradigm called literate programming, where you mix code and text to explain your code. Notebooks are widely used in data analysis, machine learning, and scientific computing because they allow you to write code, visualize data, and explain your results in a single document.
4.1 Tools for Writing Python Code
There are many tools available for writing Python code. Evaluate what works best for you! In this course, we recommend using the following tools:
- Visual Studio Code (VS Code) (code editor) + Extensions (Python, Jupyter Notebooks).
- Google Colab
- Python notebooks on Google cloud.
- Useful for sharing and collaborating on notebooks.
- No installation required.
- Computations are done on Google servers.
- Online Python Compiler (www.programiz.com)
- Online compiler to execute scripts on the browser.
- Useful for quick tests.
You can read more about Python IDEs and code editors in the following links:
- 10 Best Python IDE & Code Editors 2025 (hackr.io).
- 🎥Best Python IDE? (according to Guido van Rossum, the Python creator).
Also, if you may want to try other IDEs, such as PyCharm (free student version) or Spyder.
4.2 Why Visual Studio Code (VS Code)?
VS Code is a popular code editor that is widely used by developers for writing code in various programming languages, including Python. Here are some reasons why you might consider using VS Code:
- Lightweight and Powerful. Provides a balance between performance and functionality.
- Rich Ecosystem. Extensive library of extensions and customization options.
- Built-In Git Integration. Streamlines version control.
To install VS Code and set it up for Python programming, follow these steps:
- Download VS Code.
- Run the installer and follow the instructions.
- Launch VS Code.
Then, install the following extensions:
- Python. Provides Python language support and enables you to run Python code directly from VS Code.
- Jupyter Notebooks. Allows you to create and run Jupyter Notebooks within VS Code (watch a tutorial).
- GitHub Copilot. Provides AI-powered code suggestions and completions (watch a tutorial). You will need a GitHub account to use this extension.
- Theme Dracula Official (Optional). Changes the appearance of the editor to a dark theme.
4.3 Executing Python Code (Everywhere!)
In the following, you will run Python code using different methods. Each method is suitable for different scenarios.
4.3.1 Interactive Python Interpreter
To run Python code in the interactive Python interpreter:
- Open a terminal:
- Windows Terminal: Press
Win + R, typecmd, and pressEnter. - VS Code Terminal: Press
Ctrl + ~orView -> Terminal.
- Type
pythonand pressEnter. You should see the Python version information, as shown below:
- Enter
print("Hello World!")and pressEnter. You should see the outputHello World!. - To exit the Python interpreter, type
exit()and pressEnter.
4.3.2 Python Script (extension .py)
To run a Python script in VS Code:
- Create a new project folder (
File -> Open Folder). - Create a
hello.pyfile (File -> New File -> Python File). - Enter
print("Hello World!")and save. - Run the file:
- Option 1. Graphical Interface. Press “Run Python File” (look for a ‘play’ icon, in the top-right corner of the editor).
- Option 2. Terminal
- Open a terminal (
Ctrl + ~orView -> Terminal). - Navigate to the directory where your Python script is located. By default, the terminal opens in the root directory of the project.
- Run the script by typing
python <filename>.py(<filename>=hello.py).
- Open a terminal (
- Check result on the terminal (you should see
Hello World!).
The root directory is the top-level directory of a project. It is the directory that contains all the files and subdirectories of the project. When you open a folder in VS Code, the root directory is the folder you selected.
4.3.3 VS Code
First, make sure you have the Python extension installed in VS Code (see above). To select the Python interpreter in VS Code:
- Open the Command Palette (
Ctrl + Shift + P). - Type
Python: Select Interpreterand select it. - Choose the Python version you want to use from the list.
4.3.3.1 Running Python Scripts
To run Python code in VS Code:
- Open VS Code.
- Create a new file (
File -> New File). - Save the file with a
.pyextension (e.g.,hello.py). - Enter
print("Hello World!")and save. - Make sure you have the Python extension installed (see above).
- Run the file:
- Press
F5to run the code in debug mode. - Press
Ctrl + F5to run the code without debugging. - The output will appear in the terminal at the bottom of the VS Code window.
- Press
4.3.3.2 Jupyter Notebooks (extension .ipynb)
To run code in Jupyter Notebooks using VS Code:
- Create a
hello.ipynbfile (File -> New File -> Jupyter Notebook). - Add a code cell (
+ Code Cellbutton). - Enter
print("Hello World!")in the code cell. - Run the cell:
- Press
Shift + Enter. - Press
Execute Cell(look for a ‘play’ icon at the left of the cell). - The code within that cell will execute, and the output will appear directly below the cell.
To add text to a Jupyter Notebook:
- Add a markdown cell (
+ Markdownbutton) - Add text using the Markdown syntax. For example,
# Hello World!. - Render the formatted text:
- Press
Shift + EnterorEsc. - Press
Stop Editing the Cell(look for a ‘checkmark’ icon at the right of the cell).
- The text will be rendered below the cell.
The .ipynb extension stands for Interactive Python Notebook, IPython Notebook, or Jupyter Notebook. It is a file format that allows you to combine code execution, rich text, mathematics, plots, and rich media.
4.3.3.3 Executing Code Cells in .py Files
In VS Code, you can define Jupyter-like code cells within Python code (.py) files (see details). This feature allows you to write and test code in a more interactive way, similar to Jupyter Notebooks. You can define code cells using a # %% comment and markdown cells using a # %%[markdown] comment. For example, in a .py file, the code below:
Would produce the output presented in Figure 4.1. By cliking on the Run Cell button, you can execute the code piecemeal, as you would in a Jupyter Notebook.
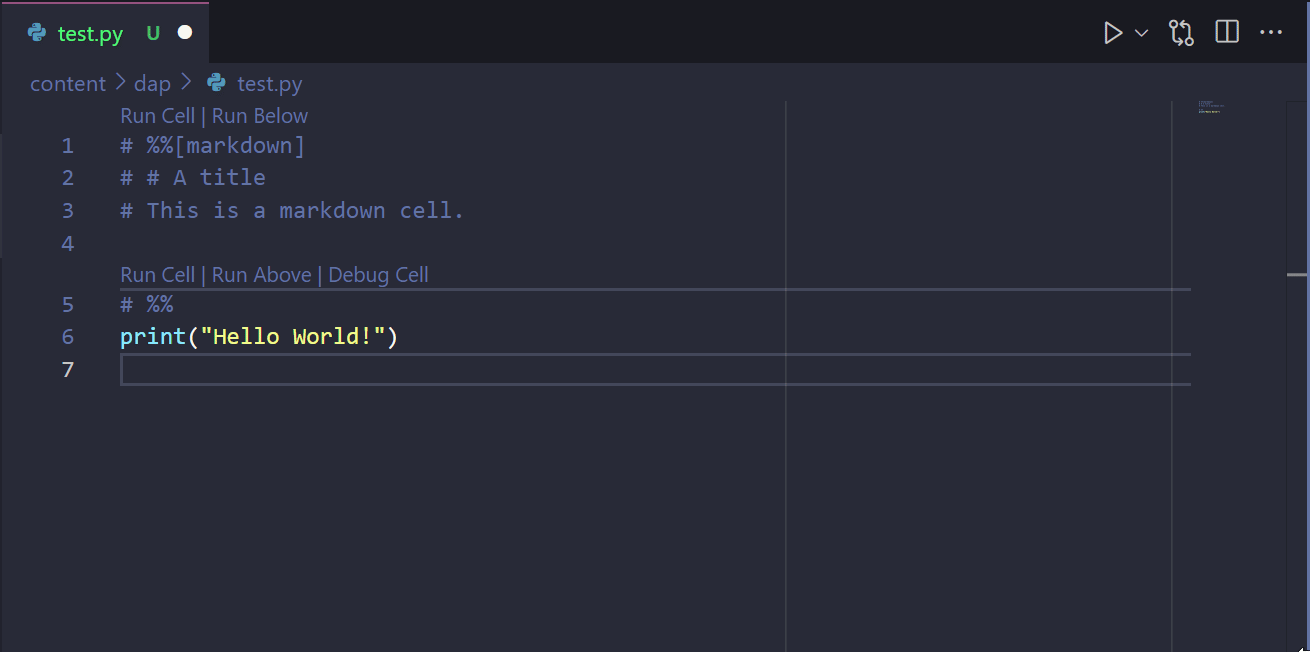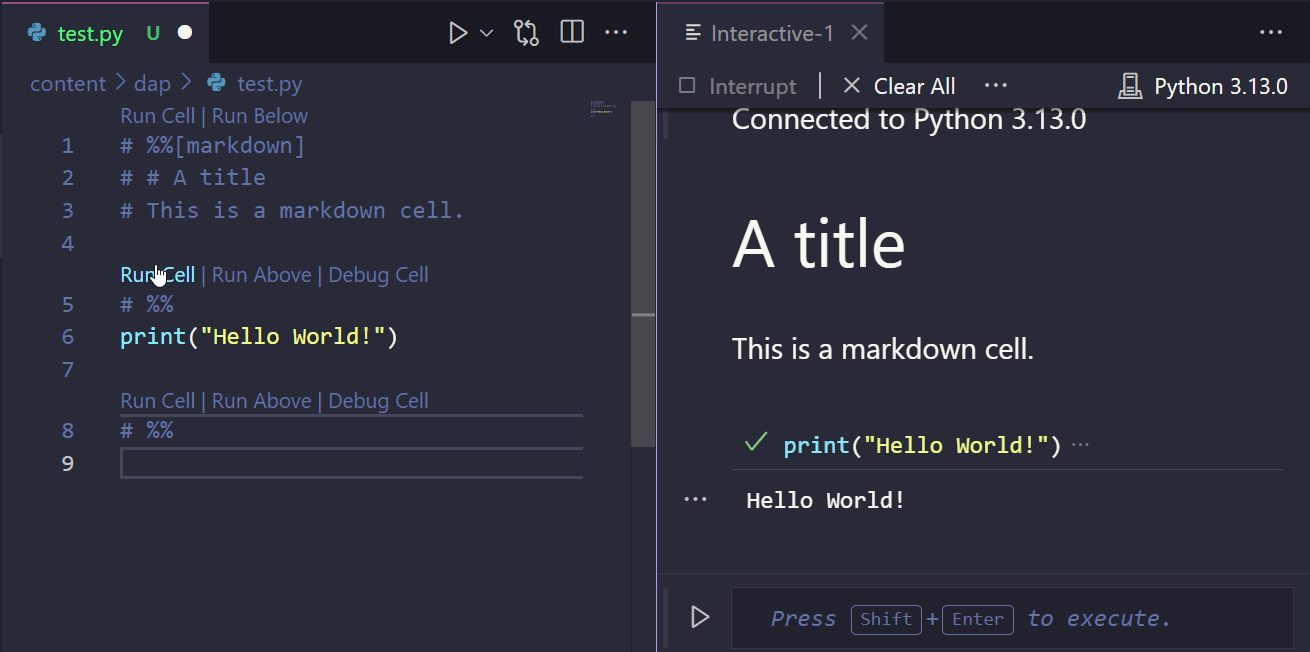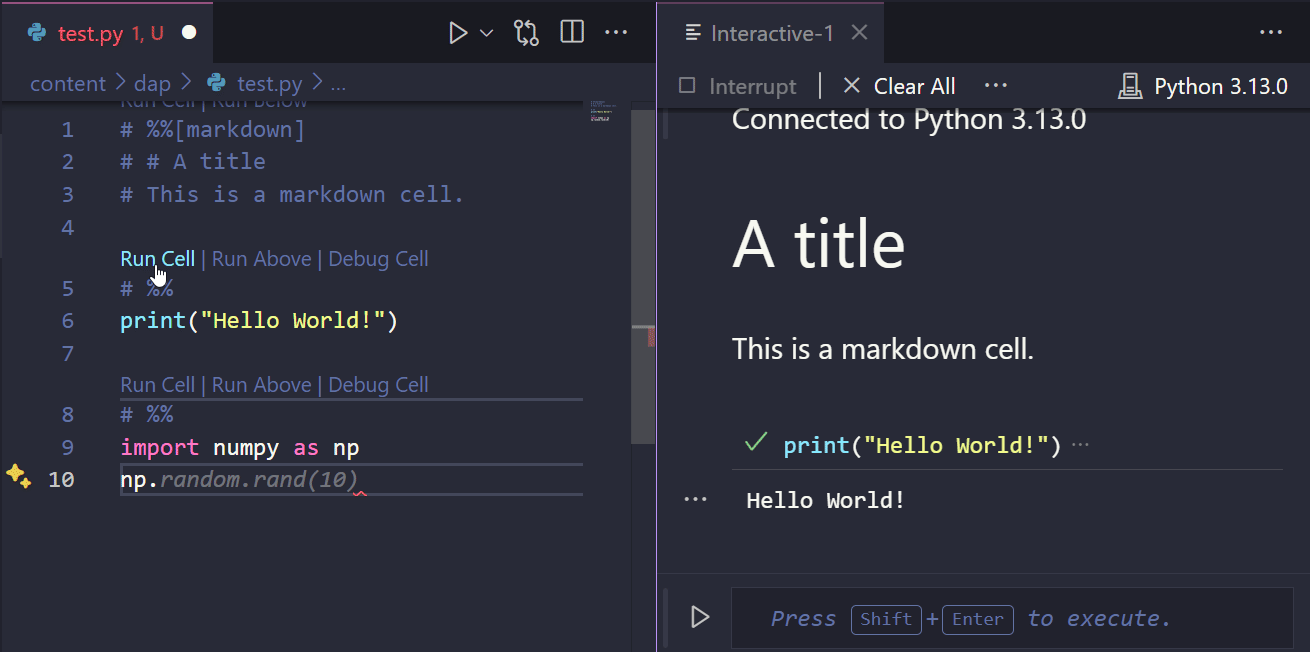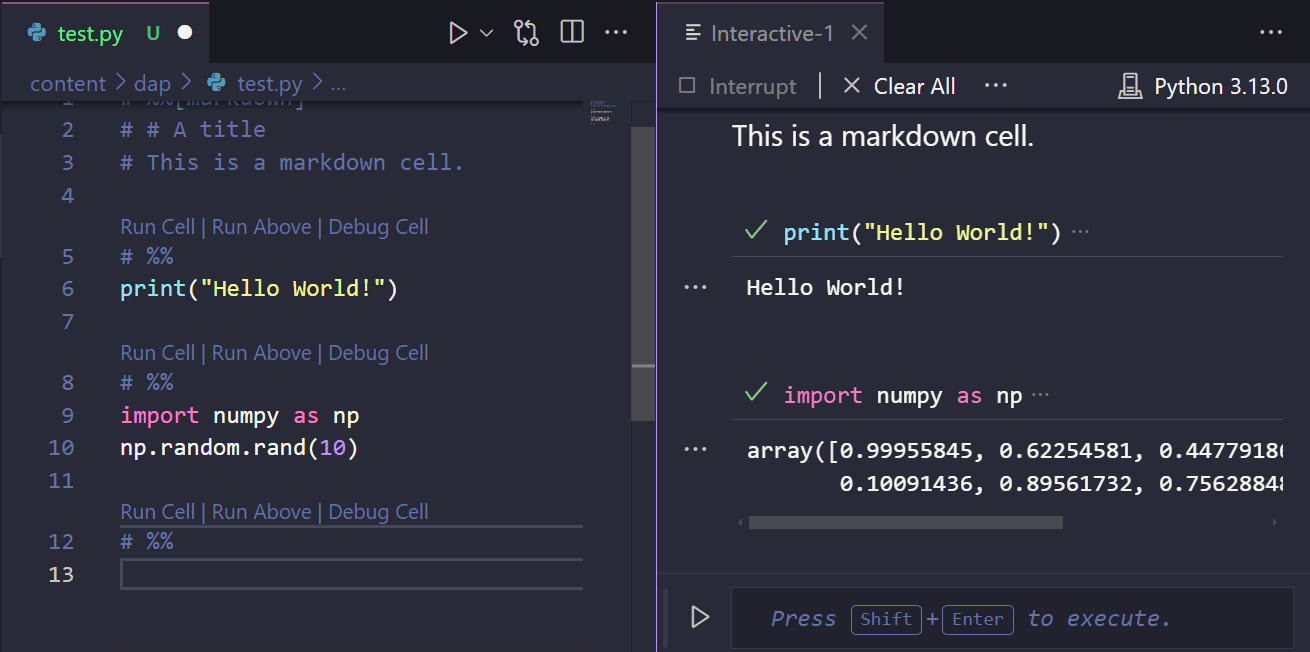
.py file. Upon running the code cells, the output is displayed in a separate window.