3 Installing Python
First, let’s check if Python is already installed on your computer. Open the terminal (in Windows, press Win + R, type cmd, and press Enter) and enter the following command:
If Python is installed, you should see the version number, like this:
If you see an error message, Python is not installed on your computer. In this case, follow the instructions below to install Python. Also, if the version number is lower than 3.14, you will need to update Python to a newer version.
Unless strictly necessary, we recommend using a single Python version for this course (e.g., Python 3.14). This will help avoid compatibility issues with packages and libraries used in the course and ensure a consistent development environment.
3.1 Removing Older Python Versions
If you have an older version of Python installed (e.g., Python 2.x or Python 3.x lower than 3.14), it is recommended to uninstall it before installing the new version. This will help avoid conflicts between different Python versions.
To uninstall Python on Windows:
- Open the Control Panel (press
Win + R, typecontrol, and pressEnter). - Click on Programs.
- Click on Programs and Features.
- Find the Python version you want to uninstall in the list of installed programs.
- Select it and click on Uninstall.
- Follow the prompts to complete the uninstallation process.
3.2 Installing a Fresh Version of Python
There are several ways to install Python on your computer (see some options here). We recommend using the official Python installer. You can download it from the official Python website.
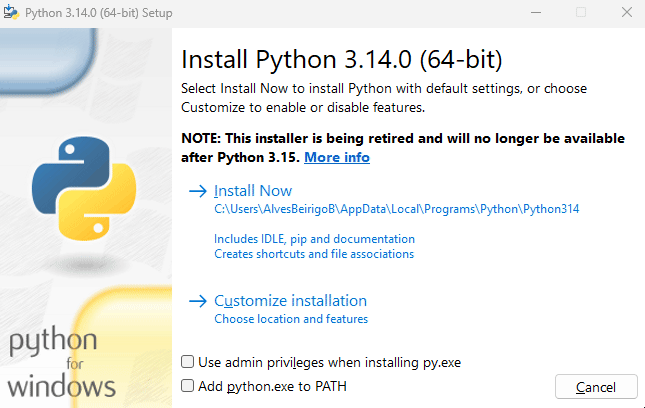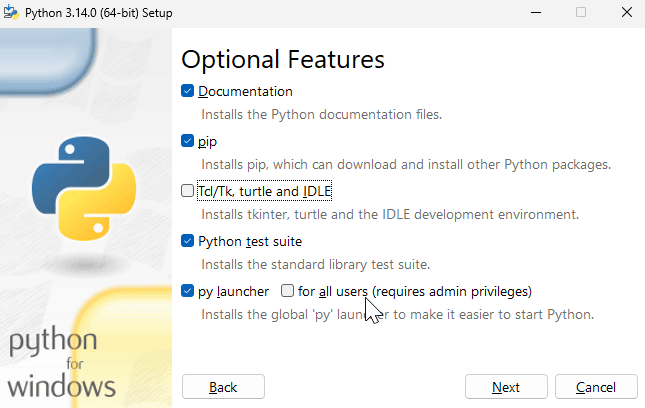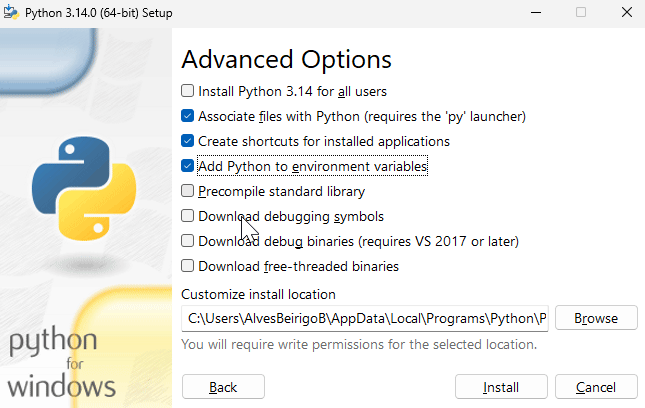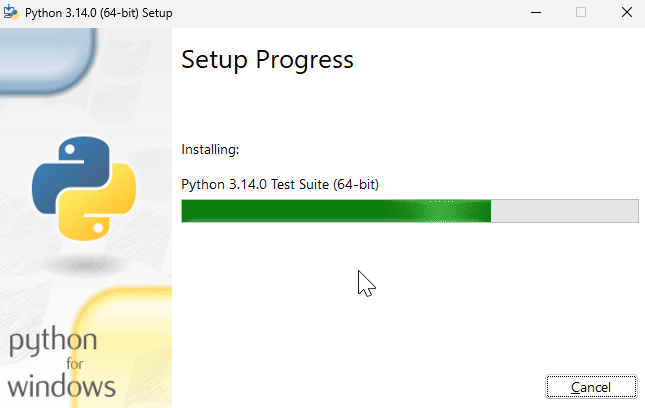
The PATH is an environment variable on your computer that specifies a set of directories where executable programs are located. When you run a command in the terminal, the operating system searches for the executable file in the directories listed in the PATH variable. By adding Python to the PATH, you can run Python from the command line without specifying the full path to the Python executable.
3.3 Troubleshooting
Below are some tips to help you troubleshoot common issues when installing Python.
These tips are fine-tuned for Windows. If you are using a different operating system, you may need to adapt the instructions accordingly.
3.3.1 Is Python Working?
To check if Python is installed on your computer:
Open the terminal (in Windows, press
Win + R, typecmd, and pressEnter).Enter
python --versionand pressEnter. If Python is installed, you should see the version number, like this:
If you see an error message, Python may not be installed correctly. In this case, you can try reinstalling Python by following the instructions above (especially the part about adding Python to the PATH).
A terminal is a text-based interface that allows you to interact with your computer using text commands. It is also known as a command-line interface (CLI). You can use the terminal to run programs, manage files and directories, and perform other tasks.
Win + R, type cmd, and press Enter. Or, search for cmd (Command Prompt) in the Start menu.3.3.2 Is The Correct Python Version Running?
If you installed Python through the official installer from python.org, you can use the py command to select the Python version you want to use.
To check the installed Python versions, run the following command in the terminal:
This command will list all installed Python versions, like this:
The asterisk (*) indicates the default Python version. If you want to run Python 3.12, use the following command, where <command> is the Python command you want to run (e.g., --version, --help, etc.):
py?
The installation via the official installer from python.org will also add the py command to your system. The difference between py and python is that py is a launcher that allows you to run different Python versions installed on your computer. For example, you can run py -3.12 to run Python 3.12, or py -3.13 to run Python 3.13.
Sometimes, other versions of Python may be installed on your computer, and the python command may still point to a different version. This can occur if Python was installed using a different method, such as the Microsoft Store. In this case, you will need to modify the PATH variable to point to the desired Python version:
- Open the Control Panel (press
Win + R, typecontrol, and pressEnter). - Click on System and Security.
- Click on System.
- Click on Advanced system settings.
- Click on Environment Variables.
- In the User variables section, look for the
Pathvariable and click on Edit. - Add the path to the Python version you want to use at the beginning of the list. For example, if you want to use Python 3.13, add the following paths (click on New for each):
C:\Users\UserName\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313C:\Users\UserName\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python313\Scripts- Make sure to replace
UserNamewith your actual username.
There might be other Python paths in the list. Make sure the path to the desired Python version is at the beginning of the list. Click OK to save the changes.
3.4 Installing Python Packages with pip
pip is a package manager for Python that allows you to install and manage Python packages. First, to update pip to the latest version, run the following command in the terminal:
To install a package, use the following command in the terminal:
For example, to install the pandas package, run:
A Python package is a collection of Python modules that can be used to add functionality to your Python programs. Packages are a way to organize and distribute Python code, making it easy to reuse code and share it with others. In this course, we will use several Python packages, including:
numpy: Numerical computing library.pandas: Data manipulation and analysis library.matplotlib: Plotting library.pytest: Testing framework.
A Python module is a single file that contains Python code. Modules can define functions, classes, and variables that can be used in other Python programs. A package is a collection of related modules that are organized in a directory hierarchy.
During this course, you will learn how to create your own modules and packages to organize your code effectively.